- Home
-
Products
Products
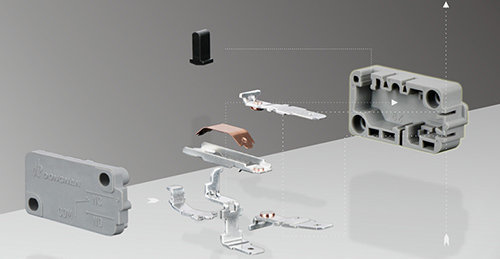
The main products of Dongnan Electronics Co., Ltd. factory include micro switches, waterproof micro switches, rotary switches, power switches, and other series. Our products have obtained UL certification in the United States, CUL certification in Canada, VDE/TUV certification in Germany, ENEC certification in the European Union, KC/KTL certification in South Korea, and COC certification in China. We have also obtained CB certificates and reports; The product is widely used in household appliances, medical equipment, low-voltage appliances, automotive parts, new energy charging equipment and other fields, with an annual production capacity of over 400 million switches.
-
About Dongnan
About Dongnan
Dongnan Electronics Co., Ltd. Headquarters Factory Southeast Electronics Co., Ltd. was founded in 1987 with stock code 301359. It is a professional switch manufacturing enterprise that integrates product research and development, production, sales, and after-sales service. Current leading products include micro switch series, waterproof switch series, rotary switch series, button type power switch, etc. All products have obtained UL certification in the United States, ENEC certification in the European Union, EK certification in South Korea, and COC certification in China. To provide customers with competitive products and satisfactory services, and to implement quality service awareness in every employee.

-
Service
Service
The factory of Dongnan Electronics Co., Ltd. aims to become a globally important enterprise in the switch industry, continuously strengthening its R&D team, and independently designing and researching inventions. Currently, it has obtained a total of 80 national patents. The company established ISO9001 quality management system in 1996, IS014001 environmental management system, OHSAS18001 occupational health and safety system in 2011, obtained QC080000 hazardous substance process management certificate in 2018, and IATF 16949 automotive industry quality management system in 2019. Quality service awareness is implemented in every employee.









 Customer Service 1
Customer Service 1